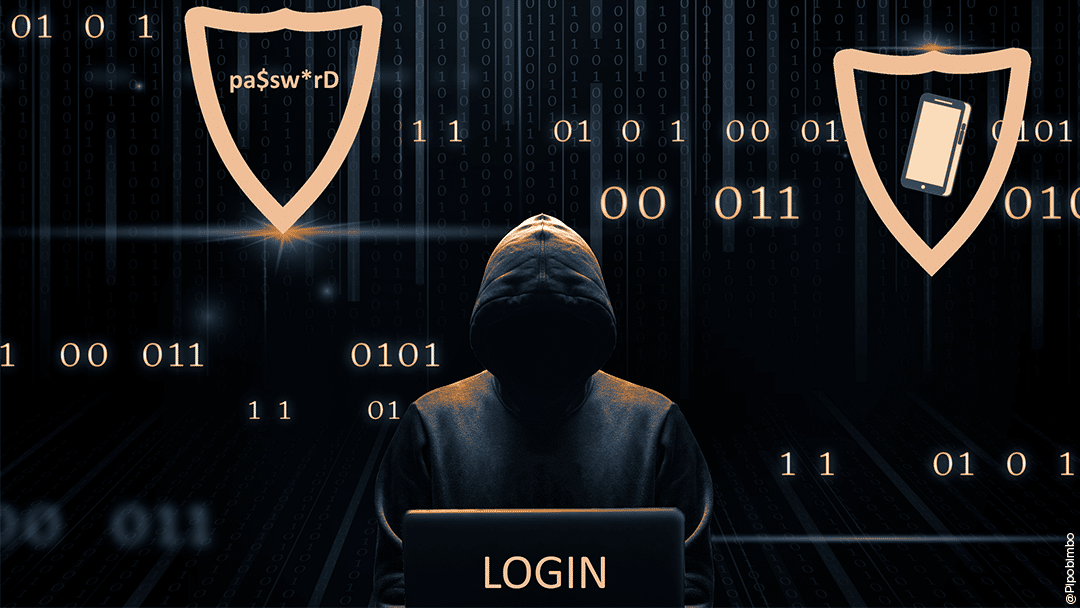
With cyberattacks continuing to increase, protecting online access has become essential for individuals and businesses alike. Data theft, account hacking and other cyberthreats are becoming increasingly common, making traditional passwords less and less secure. Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security technology that strengthens online account security by adding an extra layer of protection. But how does this technology work and why should you implement it? This article will provide you with a detailed explanation of what two-factor authentication is, how it works, what its benefits are and how to implement it effectively.
Overview
What is two-factor authentication?
Definition of two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a two-step authentication process that enhances the security of an online connection. Unlike simple authentication, which relies on a single factor (usually a password), two-factor authentication requires two distinct pieces of proof to verify a user’s identity. These pieces of proof belong to different security categories, making access more difficult for hackers.

The three main categories used for authentication are:
- Information that you know: passwords, PIN codes, or answers to security questions.
- Items that you have: a smartphone, a security token or an application that generates an authentication code.
- Your physical features: biometric features such as fingerprints, facial or voice recognition.
By combining these elements, two-factor authentication makes it virtually impossible for hackers to gain unauthorised access to your account, even if they do manage to find out your password.
Two-factor authentication components
The components within two-factor authentication increase the barriers to prevent an attack. For example, if a password is compromised, access cannot be guaranteed without access to the owner’s device. This could be in the form of an SMS, a notification in a dedicated application, or the use of a physical key. The most robust two-factor authentication solutions often combine several of these technologies to ensure maximum protection.
Why should you use two-factor authentication?
Safety benefits
The main advantage of two-factor authentication is that it makes it extremely difficult to gain unauthorised access to online accounts, if not impossible. Even if a hacker manages to obtain your password through a phishing attack or database hack, you’ll still need to provide a second factor to establish a connection. This could be a temporary code generated on your mobile phone or the use of a physical key that is virtually impossible to intercept remotely.

On the other hand, while two-factor authentication reduces reliance on passwords, they do remain vulnerable to user fraud. Many people use passwords that are too simple, or reuse the same password for different services. Two-factor authentication reduces this risk by adding an extra layer of security.
Protection against cyberattacks
Password attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, including phishing, social engineering and brute force attacks. However, even if a password is compromised, the 2FA system will deny access to the attacker unless they have a second authentication factor. This protection is essential since it blocks attempts to access the network and helps users to feel increasingly confident about their ability to protect their data.
Another important aspect is that 2FA reduces the risk of a large-scale breach following a database leak. Indeed, even if millions of passwords are stolen in an attack, users who have activated 2FA will remain protected since hackers will not be able to overcome the second authentication step.
How does two-factor authentication work?
Steps in the verification process
Two-factor authentication is a simple, straightforward process consisting of a number of different steps.
- Password authentication: first of all, the user enters their normal username and password.
- Second factor verification: after verifying the password, the user is prompted to provide a second verification factor. This may be a code sent by SMS, a code generated by the authentication application, or a physical key.
- Account access: access is granted after the second factor has been verified. If the second factor fails, access is denied, even if the password is correct.
This process guarantees the user’s identity and makes it virtually impossible for unauthorised third parties to gain access.
Commonly used technologies

- SMS: this method whereby a one-time code is sent via text message is very widespread. However, it is not without its vulnerabilities, including sim-swapping attacks.
- Authentication applications: applications such as Google Authenticator and Authy generate temporary security codes that remain valid for a short period of time (usually 30 seconds). This method is more secure than SMS, as it does not depend on the telephone network.
- Physical security keys: devices like the YubiKey need to be physically present to authorise access. This method is extremely secure since the key must be inserted into a USB port or used via NFC (Near Field Communication).
Two-factor authentication methods
Use of SMS or e-mail
Receiving an authentication code by SMS or email is a common method of two-factor authentication. This option is easy to implement and use, which is why it is so widespread. However, there are some associated vulnerabilities: for example, hackers can intercept messages using techniques such as SIM spoofing.
Authentication applications
Applications such as Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator are common tools for 2FA. These applications generate temporary codes that expire quickly, making them virtually impossible to intercept. They do not require a network connection, thereby offering enhanced security.
Physical security keys
Physical security keys, such as the YubiKey, are one of the most reliable 2FA solutions. These small, portable devices require physical interaction to take place to authenticate the connection, making them virtually invulnerable to remote attacks. They are recommended for those who need maximum security, such as businesses or people handling sensitive information.
How do I set up two-factor authentication?
Account activation steps
Activating two-factor authentication differs slightly from one service to another, but the general procedure is similar:
- Access the security settings for your online account.
- Find the 2FA or “two-step verification” option.
- Select your authentication method: SMS, application or physical key.
- Follow the instructions to connect your phone or set up a security key.
- Test the process to make sure everything is working properly.
Best practices for optimal use
To maximise security, we recommend using a backup method such as emergency codes and/or configuring workarounds such as an additional security key or installing the application on several devices.
Challenges and limits of two-factor authentication
Potential disadvantages
Like other technologies, two-factor authentication does have its disadvantages.
- Loss of access: if you lose your phone or security key, recovering access to your accounts can be complicated if you don’t have backup codes in place.
- Disadvantages for the user: some users may find it tedious to have to validate each connection using a second factor.
Solutions to overcome these challenges
These disadvantages can be mitigated by:
- Using emergency codes that you can register when you activate the 2FA.
- Configuring backup methods, such as a second security key or the addition of several trusted devices.
Qim info helps you improve the security of your systems
At Qim info, we specialise in helping companies strengthen the security of their IT systems. We offer solutions that are tailored to your needs, including the implementation of two-factor authentication on your corporate networks and accounts. We help you choose the best methods for securing your access and train your teams to ensure they follow best security practices.
To find out more about our services, visit our dedicated IT security page or contact us to discuss your data protection and cybersecurity needs.